Introduction to Common Printing Techniques
Things to Consider When Designers Create Print Files
Designers need to prepare print-ready files that can be used directly without the need for flipping.Designers and print solution designers often find themselves puzzled when initially engaging with printing factories. They wonder, as designers, whether it is sufficient to understand basic printing concepts and principles. What relevance do the characteristics and differences of each printing technique have to their actual work?
Understanding printing principles and techniques is essential for designers and print solution designers, with two primary reasons:
Developing correct print solutions
Avoiding printing risks
Print solution designers need to develop reasonable print solutions based on client requirements and budgets. Understanding printing principles and techniques helps them choose appropriate printing methods, materials, and processes, while providing accurate cost estimates.
Print solution designers need to be aware of potential risks during the printing process and take measures to mitigate them. For example, they need to consider factors such as material compatibility, complexity of printing techniques, and production capabilities of printing factories.
Through this article, designers will gain insight into the characteristics, principles, practical applications, and document requirements of commonly used printing techniques in large printing factories.
Offset Printing
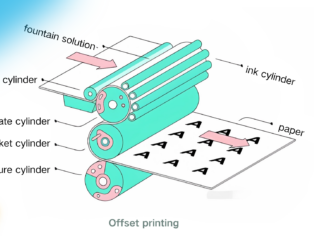
Offset printing is a method of using a flat printing plate to transfer ink onto a substrate. It is widely used in various commercial printing applications and is also known as "indirect printing."
Applications
Offset printing is extensively used by large printing companies to develop reasonable print solutions based on client requirements and budgets. Understanding printing principles and techniques helps them choose appropriate printing methods, materials, and processes, while providing accurate cost estimates.
Characteristics and principles
Both text and non-text areas are almost on the same plane.
Ink is retained only in the text and image areas, using the principle of oil-water repulsion.
The most common printing method is offset lithography.
Letterpress Printing
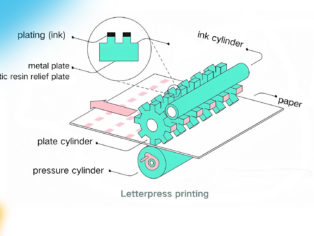
Letterpress printing transfers ink onto a substrate using raised text and image elements. It is one of the oldest printing methods.
Applications
Letterpress printing is commonly used for books, magazine covers, and specialized printing, such as business cards and greeting cards.
Characteristics and principles
Text and image elements are raised, higher than non-text areas.
Ink is applied only to the raised portions and transferred to the substrate through pressure.
Document requirements: Designers need to prepare print-ready files that can be used directly without the need for flipping.
Gravure Printing
Gravure printing is a method in which text and image elements are recessed, and ink is filled into the recessed cells and transferred to the substrate through pressure.
Applications
Gravure printing is used for banknotes, stamps, and high-end packaging printing due to its high anti-counterfeiting properties and artistic expression.
Characteristics and principles
Textext and image elements are recessed, and ink is filled into the recessed cells.
Ink is transferred to the substrate through pressure.
Document requirements
Designers need to prepare print-ready files that must be reversed, meaning the text and images should be white, while the background should be black.
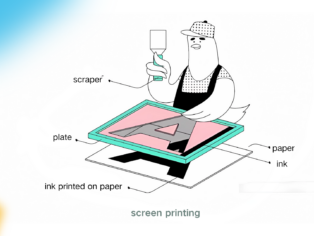
Screen Printing